
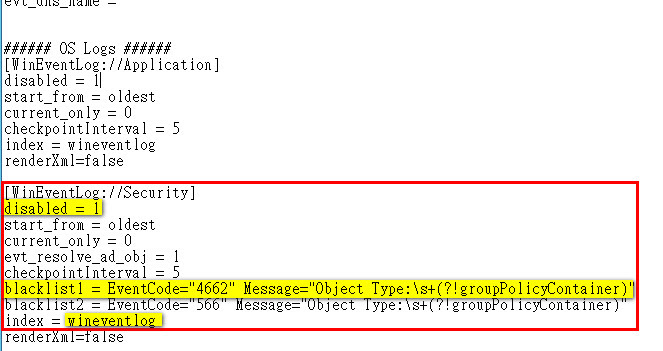
In this way, the Splunk platform assumes that each path name contains unique content. If you configure the crcSalt setting to, you ensure that each file has a unique CRC. Use the crcSalt setting when you configure the input for the file in the nf configuration file.Use the initCrcLength setting in the nf configuration file to increase the number of characters that the CRC uses for its calculation, and make it longer than any static header that might be present in the file at the beginning.To handle such situations, make the following changes: The file is a different file that begins with the same content.īecause the database for content tracking is keyed to the beginning CRC, it can't track progress independently for the two different data streams and requires further configuration.īecause the CRC start check runs against only the first 256 bytes of the file by default, non-duplicate files can have duplicate beginning CRCs, particularly if the files have identical headers.The Splunk platform read some file with the same initial data, but some of the material that it read was modified in its place.If the CRC from the file beginning in the database has a match, but the content at the Seek Address location doesn't match the stored CRC at that location in the file, the file results from the following possibilities: The Splunk platform reads the new data from that point.The Splunk platform opens the file and goes to the seekAddress within the file, which is the end of the file when the Splunk platform last finished with it.The Splunk platform then completes these steps: If the CRC from the file beginning in the database has a match, the content at the Seek Address location matches the stored CRC for that location in the file, and the file size is larger than the Seek Address that the Splunk platform stored, the file was read by the Splunk platform before but contains new data since it was last read. The Splunk platform updates the database with the new CRCs and Seek Addresses as it consumes the file.The Splunk platform reads the file data from the start of the file.

If the CRC from the file beginning in the database doesn't have a match, this indicates a new file.
The Splunk platform categorizes a file based on the following outcomes of the CRC check. How the Splunk platform categorizes a file Using the results of this lookup, the Splunk platform can categorize the file. The most important values are the seekAddress, which represents the number of bytes into the known file that the Splunk platform already read, and the seekCRC, which is a fingerprint of the data at that location. If it finds a match in this database, the lookup returns a few values about the file. The Splunk platform uses this CRC to look up an entry in a database that contains all the beginning CRCs of files that it has seen before. The processor then hashes this data into a beginning and ending cyclic redundancy check (CRC), which functions as a fingerprint that represents the file content. The monitoring processor picks up a new file and reads the first 256 bytes of the file. For example, if the Splunk platform is monitoring /var/log/messages, it doesn't also read /var/log/messages1. The Splunk platform recognizes when the operating system rotates a file that it's monitoring and doesn't read the rotated file a second time. How the Splunk platform handles log file rotation


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
